Description
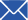
MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS belong to the category of medicines called antispasmodic, which is used in the treatment of severe stomach cramps during irritable bowel syndrome with bloating. It is a disease that directly impacts the large intestine of the body. MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS are formed by the combination of two drugs mebeverine and chlordiazepoxide. Mebeverine HCl is a musculotropic antispasmodic drug without atrophic side effects whose major therapeutic role is in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. It is also indicated for the treatment of gastrointestinal spasms secondary to organic disorder.Chlordiazepoxide is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine derivative. Chlordiazepoxide has a medium to long half-life but its active metabolite has a very long half-life. The drug has amnestic, anxiolytic, hypnotic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
You are strictly recommended not to give MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS to children without the consultation of your doctor as it can cause harmful consequences on the body. Also, do not increase or decrease the dose on your own. Talk to your doctor before you yo do so. They may provide you with some other alternative for the drug.
MECHANISM OF ACTION for MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
As a diuretic, chlorothiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the Na-Cl cotransporter, increasing the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like chlorothiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of chlorothiazide is less well understood although it may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
Side Effects of MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
Some of the side effects which which you might have to suffer after you consume these tablets are mentioned below:-
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Slurred speech
- Tiredness
- Lack of coordination
- Difficulty in controlling movements of the body
Precautions with MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
Make sure to read the precautions before consuming any drug.
- Make sure not to consume this drug before you drive or perform any kind of activity as it can make you unconscious
- Do not immediately stop taking this medication. Decrease the amount of dosage first and must discuss it with your doctor before you have to end the course for this drug.
- MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS are strictly restricted for children who are below the age of 18 years. If your physician has prescribed it, you must discuss it once.
- Tell your doctor beforehand if you had any kidney or liver disease in the past as some drugs can leave a major impact on some body organs.
- Let your doctor know if you had any allergic reactions to any kind of medicine before.
- Avoid taking this medicine if you are a breastfeeding mother as it can harm the fetus. Your doctor may prescribe you with some other alternative.
Drug Interactions of MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
You are advised not to take this drug before or after you take any other medication. If done so, drugs can interact with each other and can leave adverse effects. Some of the drug interactions for MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS are:-
- WARFARIN
- DIAZEPAM
- PHENOBARBITONE
- PHENYTOIN
- RIFAMPICIN
- BACLOFEN
- LEVODOPA
- CIMETIDINE
- OMEPRAZOLE
- CHLORPHENIRAMINE
INDICATIONS for MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
Here are some of the uses of these tablets:-
- For treating the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and similar problems such as chronic irritable colon, spastic
- For constipation, mucous colitis and spastic colitis.
- For relieving the spasms, pain, and other symptoms of IBS.
Storage of MEBEVERINE HCL 135mg & CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE 5mg TABLETS
Do not keep this drug in direct sunlight or heat. Store it at room temperature or in a cool dry place and keep it away from moisture. Also, keep it out of the reach of children and pets.